App Config
How To Configure
Configuration is a customization that your end-customers can store for each of their integrations. You can create a new dataslot to store a value from
selected or entered by your users. Some examples of dataslots are:
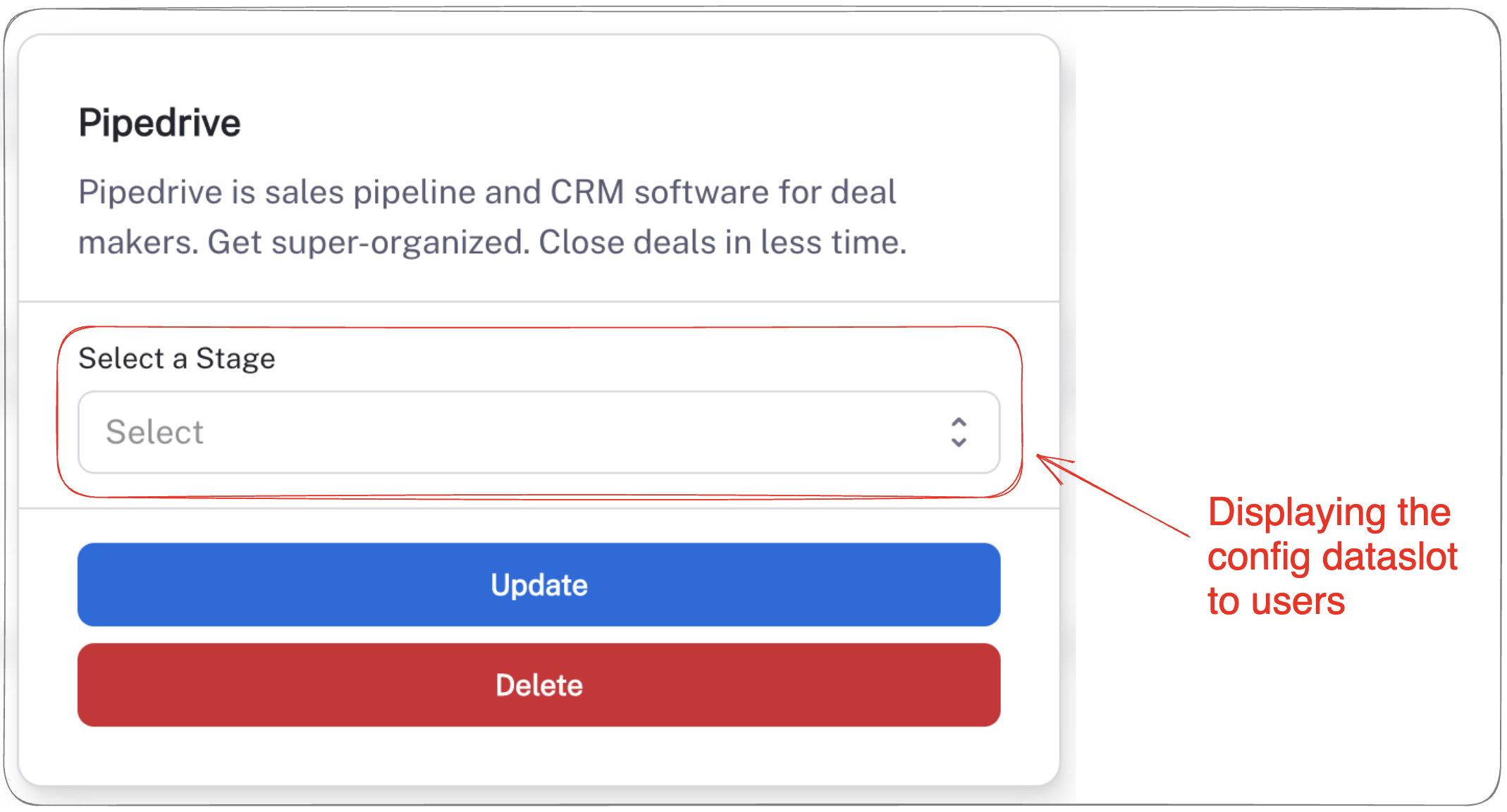
 There are different three types of config dataslots: Select, mapping and text. Look at the below example to set a new config dataslot.
Similarly, while calling the updateConfig() function make sure that you also use the respective config id.
There are different three types of config dataslots: Select, mapping and text. Look at the below example to set a new config dataslot.
Similarly, while calling the updateConfig() function make sure that you also use the respective config id.
- Slack - Select a channel where messages will be posted
- Greenhouse/Lever - Select a job where candidates will be added
- Hubspot/Pipedrive - Select a stage to which the deal has to be added
- Docusign - Select a template from which a document will be sent to a signer

Create config dataslots on Cobalt’s platform
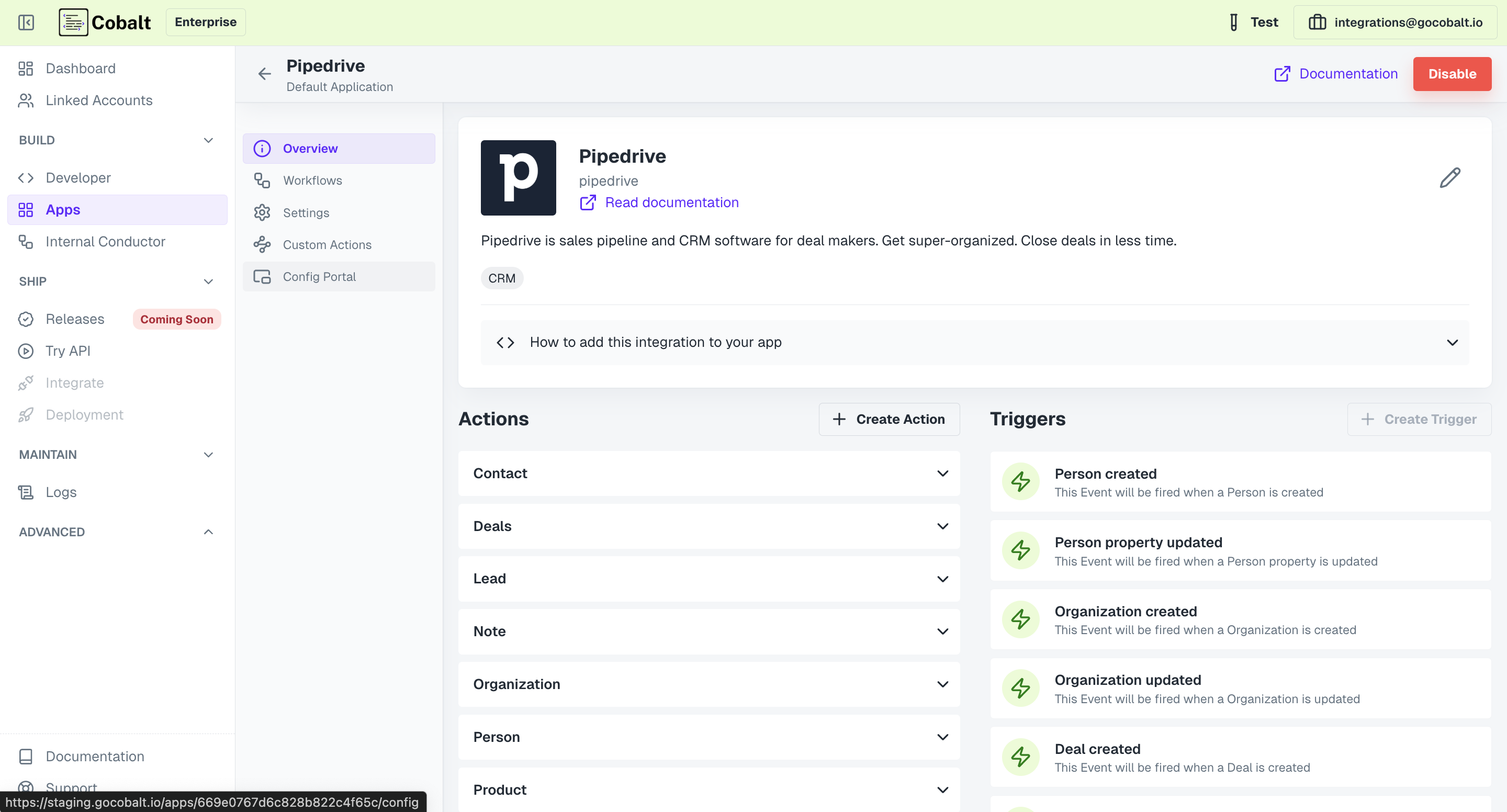
The first thing is to add a new config dataslot inside each application by clicking onConfig Portal.
 There are different three types of config dataslots: Select, mapping and text. Look at the below example to set a new config dataslot.
There are different three types of config dataslots: Select, mapping and text. Look at the below example to set a new config dataslot.