Workflows
Templating in Workflows
Overview
Cobalt supports templating (dynamic variables) in creating workflows. This essentially means that users can use these variables in their application workflows and API Proxies and authorization settings. Using these templates, users can access data from previous nodes in workflows and end-users UDF. The templates are keywords enclosed within double-curly braces{{}}, with specific use cases.
Cobalt dynamic variables and their templating can be broadly categorized as:
1. Workflow dynamic variables
Workflow dynamic variables are used to access data from previous nodes. Every node in a workflow returns some data in the form of a response object. Data from a node can be accessed either directly from the response object using a template or by accessing as variables generated through test execution of nodes:Access using template
Access using template
The following template is used within Cobalt to access the response object of any other node in the workflow: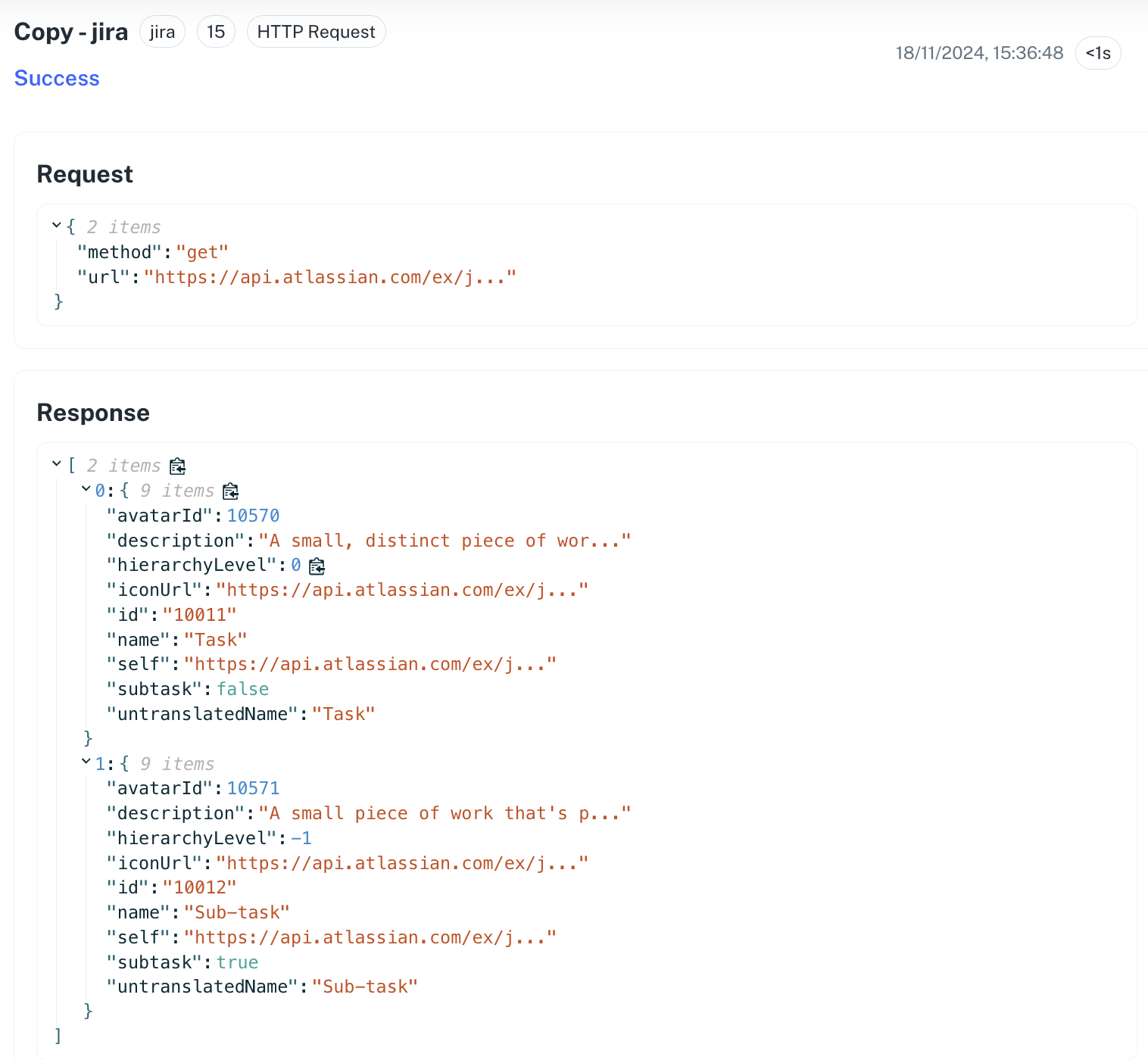 Or if one wants to access the “name” field of the item, it can be accessed as
Or if one wants to access the “name” field of the item, it can be accessed as
{{node.<node number>.body.<Response object property>}}OR{{node.<node number>.body}}, if one wishes to access the complete response object.For example, one can access the first item of response from node 15.It can be accessed as: {{node.15.body.0}}. Or if one wants to access the “name” field of the item, it can be accessed as
Or if one wants to access the “name” field of the item, it can be accessed as {{node.15.response:0.name}}.Access using Test Run variables
Access using Test Run variables
In Cobalt workflows, you can use variables generated from tested node responses to access data dynamically.To use variables generated from node test runs, ensure that the workflow testing pre-requisites are satisfied and you have run a test execution on the node whose response you want to access.Now follow the steps given below to use these variables:
Learn more about Workflow Testing and it’s pre-requisites here.
1
Select the node
Go to the node where you want to use the variable and click on the input field where the variable is needed.
2
Choose the node with required response
From the 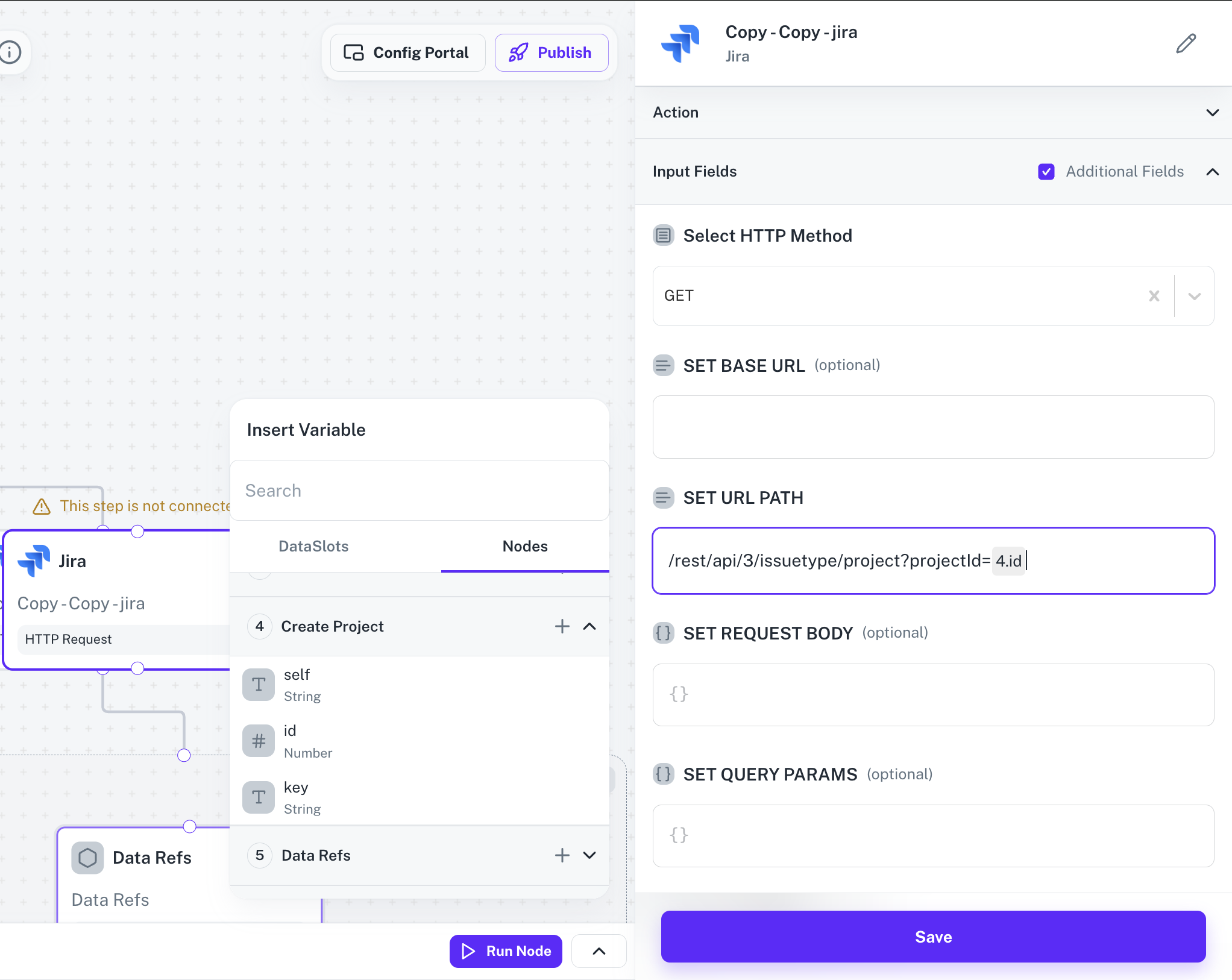 In this example, we used the
In this example, we used the
Insert Variable modal, select the Nodes tab and click on the down facing arrow button to expand the node response. In this example, we used the
In this example, we used the id received in the response when project was created and it’s visible as 4.id in the field which is of the format <node_number>.<response_field>.3
Response not available
If the selected node doesn’t have resonse as variables, then you need to click on 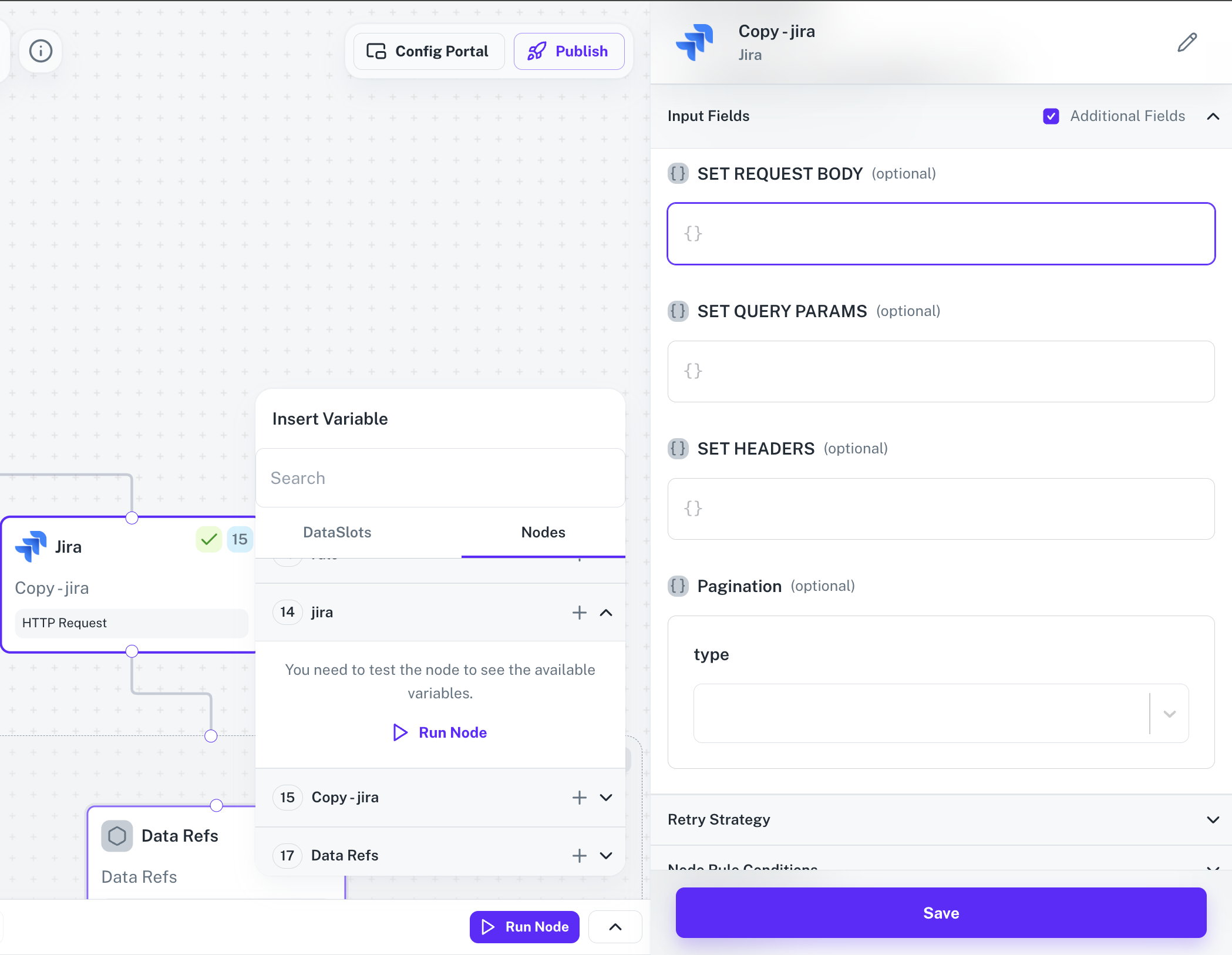
Run node to perform a test execution of that node.
If the structure of the response object changes of a node (e.g., due to a different input payload), simply perform another test run on the node with the modified payload.The updated response structure will now be available for use as variables in other nodes.
2. Instance metadata variables
An instance refers to a workflow execution instance. A workflow or an API proxy can access various instance data on the run-time such as,-
Event name -
{{instance_meta_data.event_name}} -
Config id -
{{instance_meta_data.config_id}} -
Start time of the execution / Instance creation -
{{instance_meta_data.instance_created_time}} -
Instance id -
{{instance_meta_data.instance_id}}
3. Linked account variables
Linked account variables are used to pass on Linked account-specific data throughout the Cobalt platform. The following are the variables that be used on the execution runtime:-
UDFs -
{{linked_account.udf.<UDF property>}} -
Authorization data -
{{linked_account.auth_credentials.<auth properties>}}