Triggers
Intro to Workflow Triggers
All workflows start with a trigger.
Trigger determines when the workflow will run and how data is passed into the workflow. Triggers are setup in the
 Once deployed, the workflow will run automatically at the designated time for all users who have activated the workflow.
Once deployed, the workflow will run automatically at the designated time for all users who have activated the workflow.
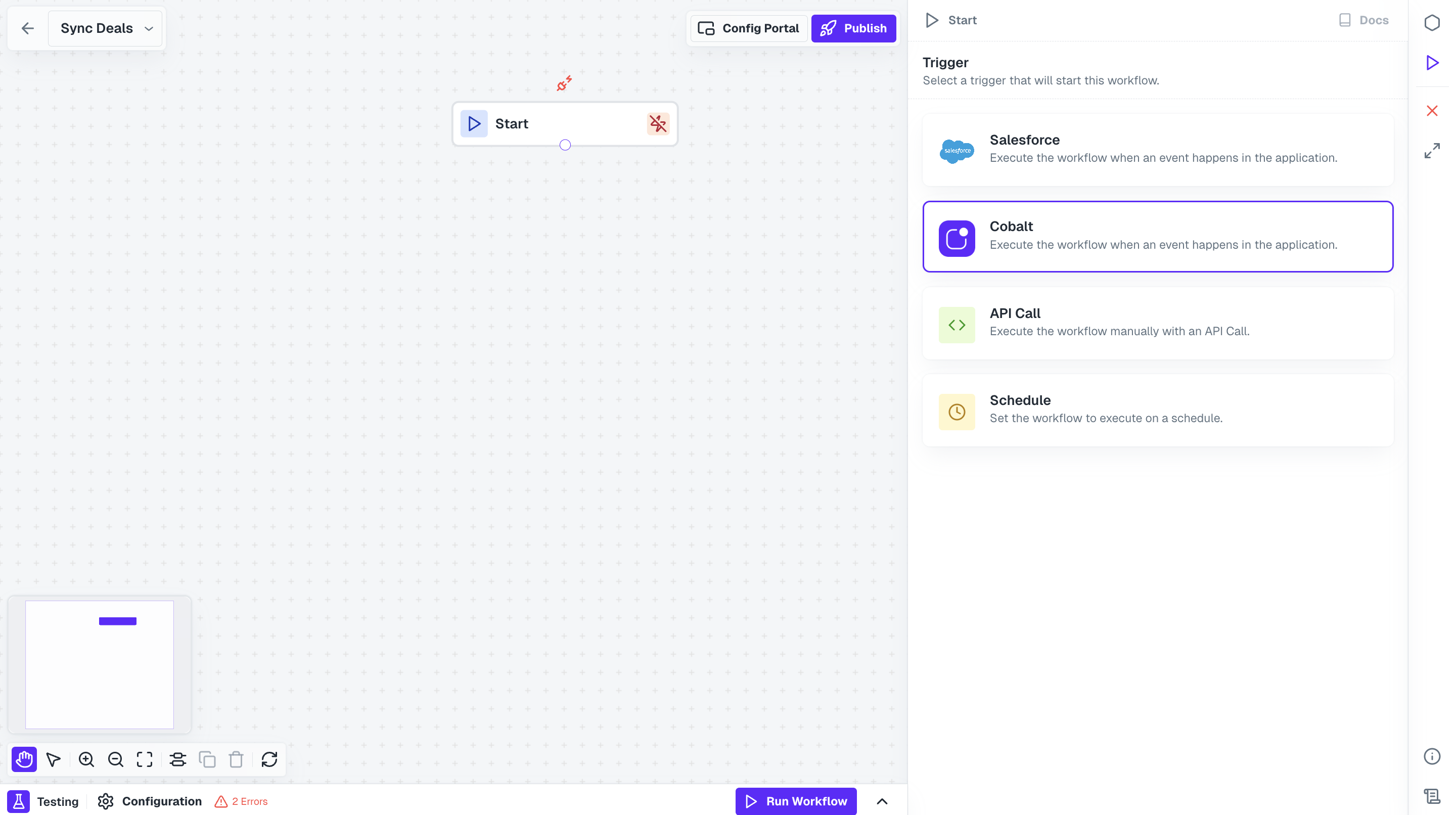
Start Node of workflow. Following are the available workflow trigger types.
App Events
App Events are custom events that are sent from your application via the Cobalt SDK or API to trigger Workflows. In general, App Events are useful for triggering workflows that map data from your application to your users’ apps. For example, you might send aContact Created App Event from your application to trigger a Workflow that creates a matching contact in your users’ Salesforce CRM.
An App Event can be used to trigger multiple workflows. This is useful in cases where you may want the same event to trigger similar workflows across different integrations.

Learn more about Events in our guide here.
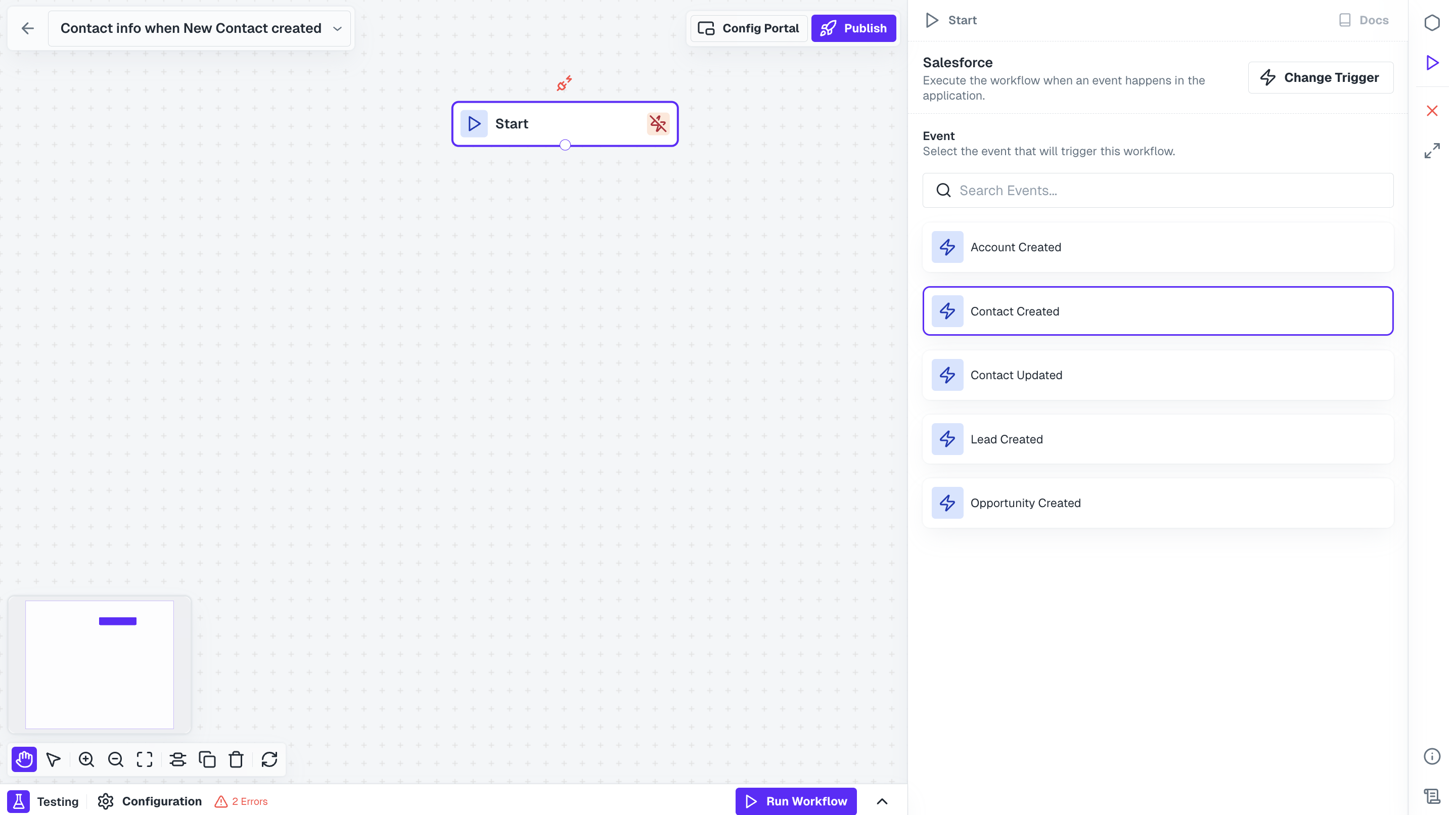
Default App Triggers
Default App triggers can be used to run workflows based on events in your users’ apps in real-time. This is achieved through the app’s webhooks and are available as Triggers in the integration. For example, you might want to trigger a workflow whenever new contacts are created in your users’ Salesforce account, to sync contacts to your application in real-time. Then this can be done by using theContact Created trigger.

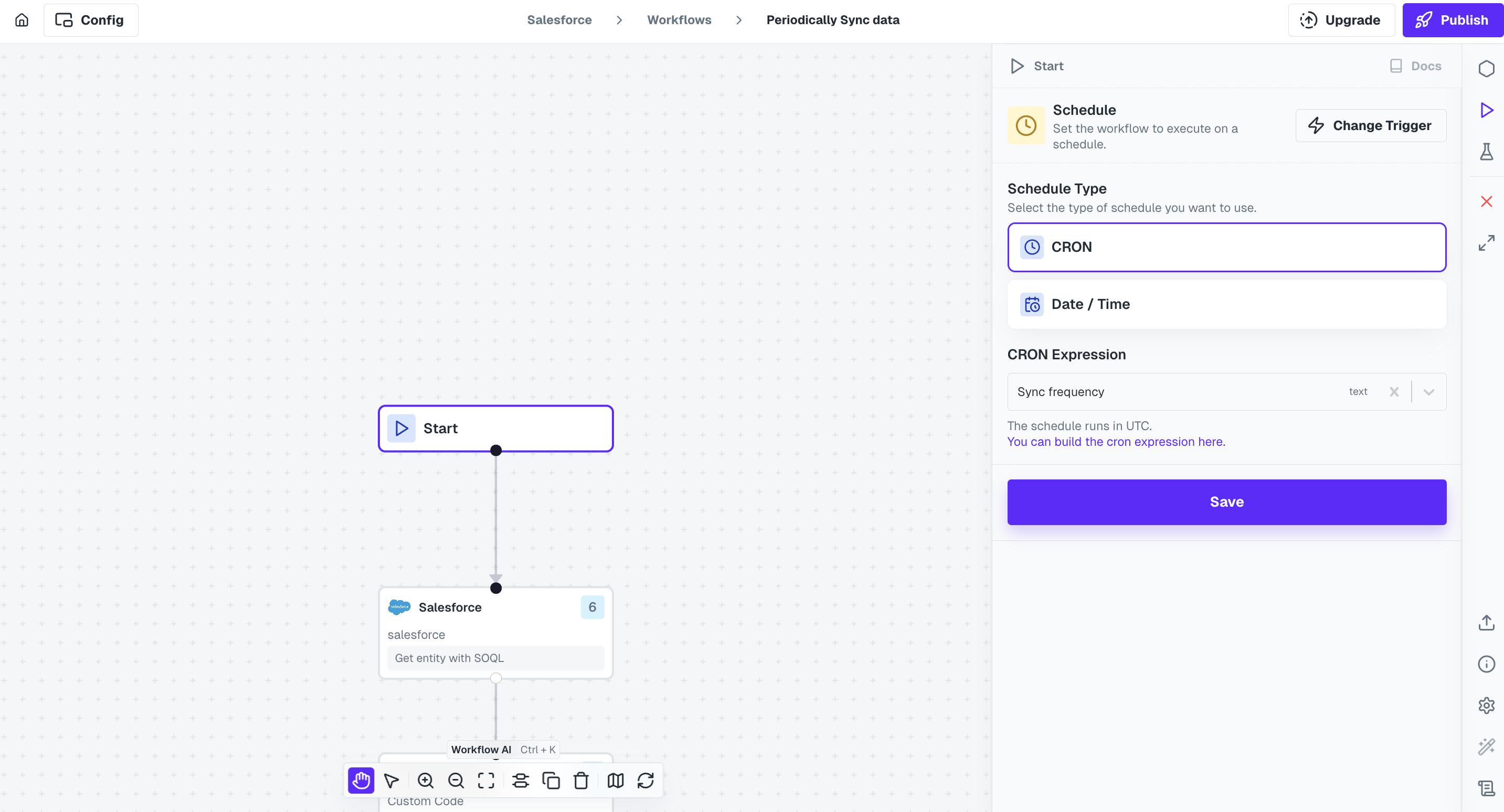
Schedule
The Scheduler trigger is used for workflows that should run automatically at a scheduled time or interval.- Minutes (e.g. every 30 minutes)
- Hourly (e.g. every hour at 15 minutes past the hour)
- Daily (e.g. every 2 days at 9:00 am)
- Date Time Intervals
Learn how to use Schedule Trigger here.

The minimum time that can be set in scheduler should be greater than 5 minutes.
Workflow API
The Workflow API in Cobalt allows users to execute workflows programmatically instead of relying on event-based triggers. This API-based execution provides flexibility in triggering workflows directly through an API call.Know more about Workflow API here.